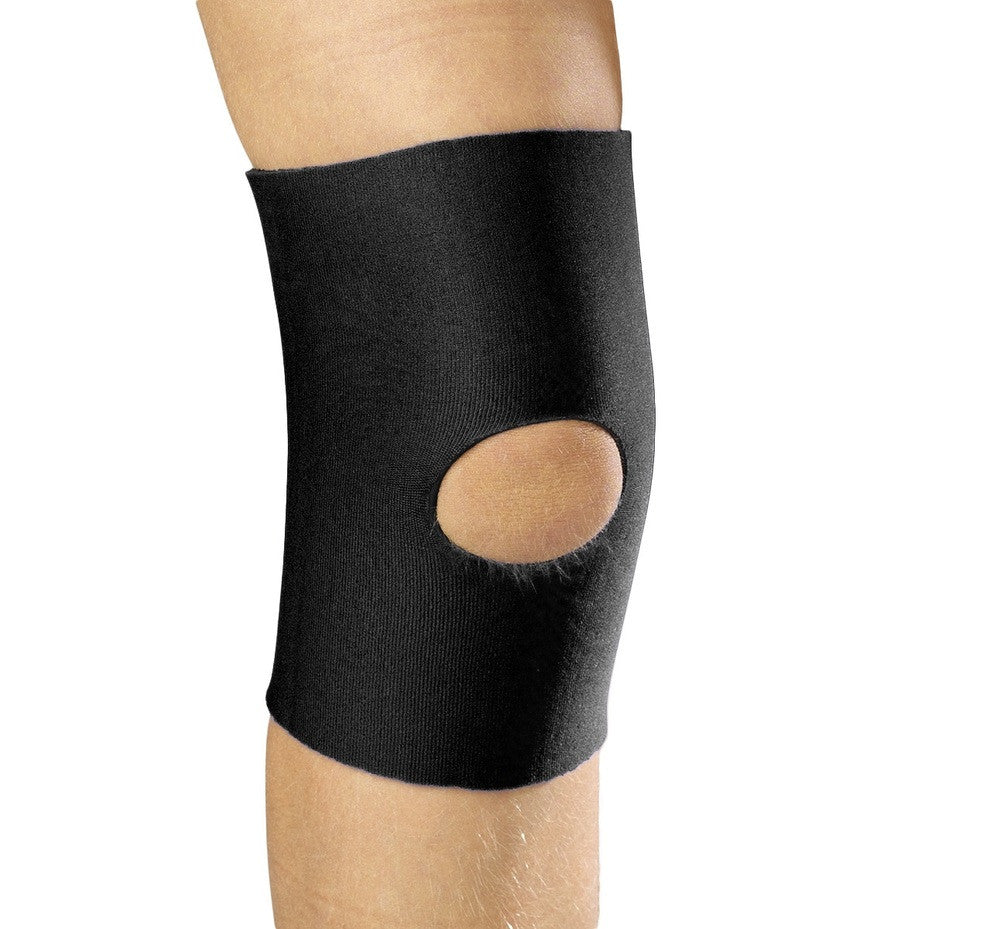
0324 / PEDIATRIC KNEE WRAP
The OTC 0324 KidsLine adjustable knee wrap is excellent for use in athletic activities or as a general use post-injury support. It has a wide range of adjustability to fit kids of virtually any age. KidsLine is OTC’s family of Pediatric and Youth sized products. They are cut and assembled to follow the anatomically correct profile as our popular adult versions, but are “right sized” to fit a smaller frame.
Indications Listed Below
• Opens flat for easy application
• Durable four-way stretch fabric for even compression over joint
• Two flexible stays on each side
• Adjustable encircling straps keep wrap in proper position
• Opening over back of knee
• Plush bilateral interior padding for extra protection around joint
• Easy contact closure fastening and adjustment
Product Features
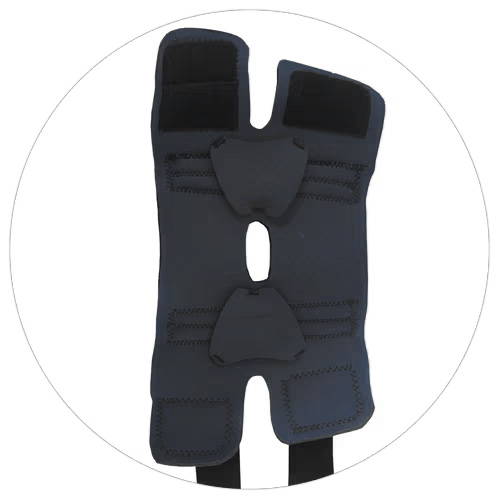

COMFORTABLE AND EASILY APPLIED
Opens flat for easy application. Plush bilateral interior padding for extra protection around joint.
ENCIRCLING STRAPS
Adjustable encircling straps keep wrap in proper position.
How to Measure for and Apply KidsLine Knee Wrap
FOR CHILDREN 2 TO 12 YEARS OF AGE
Fits 8” - 12” (20.3 - 30.5 cm) knee circumference . Knee wrap measures 7” (17.8 cm) from top to bottom.
Measuring Instructions
A. Measure around the bend of the knee
Application Instructions
1. Wrap the support around the knee until the front opening surrounds the kneecap (patella).
2. Adjust the support so the stays are correctly aligned along the midline of the knee.
3. When properly applied, the support should fit snug but not so tight that it deeply depresses the skin.
Medical Applications
Review the accompanying chart to determine the product that best suits your needs. On the left, you will find a variety of injuries that OTC products are specifically designed to treat and prevent. On the top, you will find the product numbers of all OTC KidLine Products. If a red box is present where the column and row intersect, your injury is treated by the associated product.
| MODEL NUMBER | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0316 | 0317 | 0318 | 0320 | 0321 | 0322 | 0323 | 0324 | |
| Sprains and Strains | ||||||||
| Osteoarthritis | ||||||||
| Chondromalacia | ||||||||
| Patellofemoral Tracking | ||||||||
| Mild Sprains and Strains | ||||||||
| Mild to Moderate Sprains and Strains | ||||||||
| Post-cast Support | ||||||||
| Tendonitis | ||||||||
| Carpal Tunnel Syndrome | ||||||||
| For wear post-fracture, sprain or surgery | ||||||||
| Minor neck pain or injuries | ||||||||
| Reminder against making sudden and painful movements | ||||||||
| Relief from muscle tension | ||||||||
| Whiplash | ||||||||
| To shield a lower extremity cast from moisture | ||||||||
| Shock and everyday wear | ||||||||
CRUCIATE AND COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INJURIES
The conditions shown below may not be treated by the product listed on this page. Please view the above Medical Applications Chart to determine what conditions this page's associated product treats.
ACL Injuries
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) helps maintain knee stability by preventing the tibia (shin bone) from sliding forward beneath the femur (thigh bone). It can be injured in any number of ways, for example: changing direction rapidly, slowing down while running, landing from a jump, and direct injury (such as in a football tackle).

SYMPTOMS
• A “popping”sound noted when injured
• Knee swelling within 6 hours
• Joint instability
• Pain on the medial (inner) side of the knee
PCL Injuries
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) injuries disrupt knee joint stability because the tibia can sag backwards. The PCL is usually injured by hyperextension (overextending the knee), or a direct blow to the flexed knee (the position of the knee when you bend the leg).

SYMPTOMS
• Knee swelling and tenderness in the space behind the knee (popliteal fossa)
• Joint instability
• Joint pain
MCL Injuries
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is located at the inner side the knee joint. The MCL connects the femur to the tibia and provides stability to the inner side of the knee. Injuries to the MCL are usually caused by contact on the inside of the knee.

SYMPTOMS
• Sharp pain on the medial side (inside) of the knee
LCL Injuries
The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is located at the outer side of the knee joint. The LCL connects the femur to the lateral bone in the lower leg, the fibula, and stabilizes the outer side. Injuries to the LCL are usually caused by contact to the outside of the knee.

SYMPTOMS
• Pain and tenderness along the outside of the kneecap (patella)
• Possible swelling
• Chronic pain and weakness
KNEE ANATOMY

soft tissues of the knee
A. Quadriceps Muscles
The large muscle group found in front of the thigh that traverses the femur and terminates at the supra-patellar tendon. The quadriceps muscles allow the knee to extend or straighten out.
B. Supra-Patellar Tendon
Attaches to the quadriceps muscles to the patella (kneecap).
C. Menisci (Medial and Lateral Meniscus)
Fibrous cartilage pads that distribute weight and provide a smooth surface for the joint to move on.
D. Infra-Patellar Tendon
Attaches the tibia to the patella.

Ligaments of the knee
A. PCL (Posterior Cruciate Ligament)
Attaches at the back of the tibia and the front of the femur. Prevents dislocation of the femur in a forward direction.
B. MCL (Medial Collateral Ligament)
Connects the femur to the tibia and provides stability to the inner side of the knee.
C. ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament)
Attaches at the back of the femur and the front of the tibia. Limits rotation and forward movement of the tibia.
D. LCL (Lateral Collateral Ligament)
Connects the femur to the fibula and stabilizes the outer side of the knee.